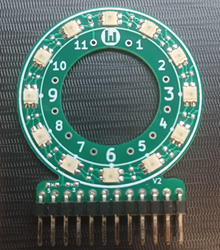
玩學運算科技有出品一種燈環套件,是使用 12 顆 LED 燈構成的電路板。這個燈環的運作原理是跟 WS2812 LED 一樣。在這個套件中,驅動這個燈環的腳位是 Pin 2,寫程式時要記得修改,不要照抄別地方的範例程式,卻發現不能執行。

什麼是 WS2812B 呢? WS2812B 是一種廣泛應用於 LED 燈帶或是LED 燈板照明應用的智慧型燈珠。具有相當多特色與優點,廣受市場歡迎,特色如下:
WS2812B LED 您可以在此連結下載技術文件。而這種LED 又常被稱為「NeoPixel」。Neopixel 內部實際上有3個LED(紅色、綠色與藍色)燈,和一個微小的控制電路。

Micropython NeoPixel 的文件在兩個地方,主要有「NeoPixel driver」與「Controlling NeoPixels 」我們先看 Driver 這邊的原始碼:
from machine import Pin
from neopixel import NeoPixel
pin = Pin(12, Pin.OUT) # 這邊我們要修改為
np = NeoPixel(pin, 12) # 玩學機燈環的數目為 12
np[0] = (255, 255, 255) # 設定LED燈為白光
np.write() # 將數值輸出,即為點燈
r, g, b = np[0]
另外在「Controlling NeoPixels」處,有提到一個很重要的地方。就是我們要控制 NeoPixels 需要先引入幾個重要的函式庫。
另外NeoPixel模組支援超過3種顏色的燈,像是 RGBW或 RGBY,使用 bpp 參數來控制。如果是四色燈,就用「bpp=4」,來初始化物件。但我們用的燈環是 RGB的形式,所以我們使用「bpp=3」,來設定每個燈的顏色。
像我們要讓第一個燈變成紅色,可以執行這樣的程式碼,np[0] = (128, 0, 0)。
import time
from machine import Pin
from neopixel import NeoPixel
pin = Pin(2, Pin.OUT)
np = NeoPixel(pin, 12)
for i in range(0, 12):
np[i] = (64, 0, 0)
np.write()
time.sleep(1)
np[i] = (0, 0, 0)
np.write()
import time
import machine, neopixel
np = neopixel.NeoPixel(machine.Pin(2), 12, bpp = 3)
def demo(np):
n = np.n
# cycle
for i in range(4 * n):
for j in range(n):
np[j] = (0, 0, 0)
np[i % n] = (255, 255, 255)
np.write()
time.sleep_ms(25)
# bounce
for i in range(4 * n):
for j in range(n):
np[j] = (0, 0, 128)
if (i // n) % 2 == 0:
np[i % n] = (0, 0, 0)
else:
np[n - 1 - (i % n)] = (0, 0, 0)
np.write()
time.sleep_ms(60)
# fade in/out
for i in range(0, 4 * 256, 8):
for j in range(n):
if (i // 256) % 2 == 0:
val = i & 0xff
else:
val = 255 - (i & 0xff)
np[j] = (val, 0, 0)
np.write()
# clear
for i in range(n):
np[i] = (0, 0, 0)
np.write()
demo(np)

# 彩燈骰子
import time
import neopixel
# 蜂鳴器啟動
machine.Pin(17, 2).value(1)
snd = machine.PWM(machine.Pin(25,2))
snd.duty(0)
def play(f, t):
snd.freq(f); snd.duty(50)
time.sleep(t); snd.duty(0)
# 燈環控制
numbers = 12
np = neopixel.NeoPixel(machine.Pin(2), numbers, bpp = 3)
wb.cls()
while True:
if wb.getkey() > 0:
count = wb.rand() % 100 + 20
for i in range(1, count):
np[i%numbers] = (64, 0, 0)
play(880, 0.02)
np.write()
wb.str(str(i%numbers), 10, 20, 2, 15)
if i == count-1:
print('')
else:
wb.cls()
np[i%numbers] = (0, 0, 0)
time.sleep(0.01)
玩了好幾個LED範例,是不是覺得很炫呢?明天我們要解釋聲音產生的原理與程式。請繼續「遊戲音樂引擎展示」的課程。明天見!
